In the realm of surface finishing, "powder coating powder" has emerged as a revolutionary technology that transforms the way we protect and beautify various materials. As industry expert Dr. Emily Carter states, "Powder coating powder provides not only durability but also an array of design possibilities that traditional liquid coatings simply cannot match." This powerful technique utilizes finely ground particles of pigment and resin, which are electrostatically charged and applied to a substrate, creating a resilient finish upon curing.
The versatility of powder coating powder makes it suitable for a myriad of applications, from automotive parts to household appliances and even architectural elements. By using this method, manufacturers can achieve a finish that is not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly resistant to environmental factors such as corrosion and wear. As businesses and consumers alike continue to seek sustainable and efficient finishing solutions, understanding the principles and benefits of powder coating powder becomes essential. This article will explore the workings of powder coating powder, its applications, and why it is becoming the go-to choice in the finishing industry.

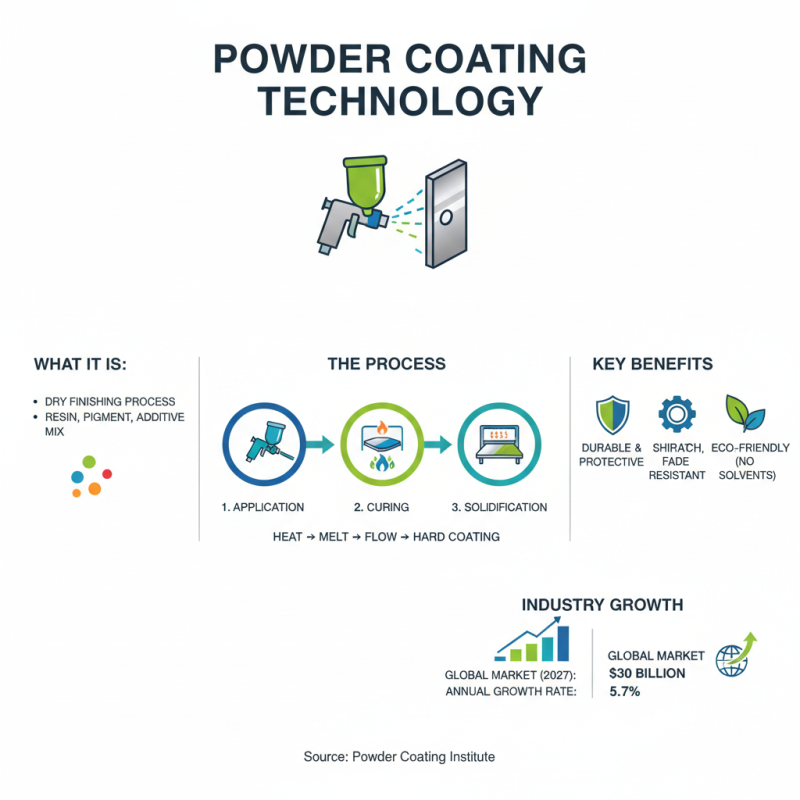
Powder coating powder is a type of dry finishing process that offers a durable and aesthetically appealing surface for various substrates. Unlike conventional liquid paint, powder coating is formulated as a free-flowing, dry powder made from a mixture of resins, pigments, and additives. When heated to high temperatures, the powder particles melt and flow into a smooth coating, which then solidifies upon cooling. This process transforms powders into a hard protective layer, which is resistant to chipping, scratching, and fading. According to the Powder Coating Institute, the powder coating industry has been experiencing rapid growth, with the global market expected to reach approximately $30 billion by 2027, reflecting an annual growth rate of 5.7%.
In many applications, powder coating proves to be a versatile finishing option. Its use spans across industries, including automotive, aerospace, and furniture, where durability and aesthetics are paramount. Reports suggest that approximately 15% of all coatings used worldwide are powder coatings, highlighting their increasing adoption due to superior performance characteristics. One notable advantage of powder coating is its environmental friendliness; it produces little to no volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it a favorable choice for manufacturers seeking to minimize their ecological footprint. Furthermore, the application process is highly efficient, generally resulting in less waste as excess powder can be collected and reused, enhancing both economic and environmental sustainability within various sectors.
Powder coating is a complex process that involves the application of a dry polymer resin to a surface, followed by curing to create a durable finish. The key components of powder coating are primarily thermosetting and thermoplastic materials. Thermosetting powders, which are the most common, consist of polymers such as epoxy, polyester, and acrylic, each providing specific properties such as corrosion resistance, flexibility, and enhanced durability. These powders are formulated with pigments, fillers, and additives that not only contribute to the color and texture but also enhance performance characteristics, making them suitable for different environments.
The powder coating process starts with the application of the powder to a clean, electrically charged surface using an electrostatic spray gun. The charged particles adhere to the substrate, which is then subjected to heat in an oven. During this curing phase, the powders melt and chemically react, forming a continuous film that bonds to the surface. This transformation not only results in a hard and resilient coat but also allows for better coverage of intricate shapes and surfaces. Understanding the chemistry behind these key components and processes is essential for optimizing powder coating applications in industries ranging from automotive to consumer goods, ultimately leading to improved durability and aesthetic appeal.
Powder coating is a popular finishing process that applies a protective and decorative coating to various substrates, and it involves several key application methods that enhance its effectiveness across different settings. The most common techniques include electrostatic spray, fluidized bed, and corona charging. Electrostatic spray painting uses an electric charge to attract powder particles to the object being coated, ensuring even coverage and minimal waste. This method is particularly effective for intricate designs and components with complex shapes.
In addition to spray techniques, fluidized bed coating is another widely utilized method, particularly for smaller parts. This process involves submerging a heated object into a bed of powder that is being agitated, allowing the powder to adhere and melt onto the surface, achieving a thick and durable finish. Each application method has its unique advantages, making it essential to choose the right technique based on the specific requirements of the project.
**Tips:** When deciding on an application method, consider factors such as the size and shape of the item, the desired thickness of the coating, and production speed. Ensuring proper surface preparation before coating can also significantly enhance adhesion and reduce the likelihood of defects. Additionally, maintaining the equipment regularly will help achieve better results and prolong the lifespan of the application tools.
Powder coating has emerged as a preferred finishing technique across various industries, owing to its durability and environmental benefits. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global powder coating market size was valued at approximately $11.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6.5% from 2023 to 2030. This growth can be attributed to the increasing demand for eco-friendly coatings and the expanding applications of powder coating in industries such as automotive, furniture, and construction.
In the automotive sector, powder coating is favored for its ability to provide a tough, chip-resistant finish that withstands harsh conditions. The automotive industry alone accounted for about 30% of the total powder coating market in recent reports, reflecting a significant reliance on this technology for both aesthetic and protective purposes. Furthermore, in the furniture industry, powder coating enhances longevity and visual appeal, making products more resistant to scratches and corrosion. The versatility of powder coating allows it to be applied on diverse substrates, which contributes to its proliferation across applications, including household appliances and even architectural elements. These advantages underline how powder coating excels in creating sustainable and high-performance finishes tailored to meet the specific needs of varied sectors.
| Application Sector | Benefits of Powder Coating | Common Substrates | Durability Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | High resistance to scratches and chemicals | Metal parts, frames, wheels | Corrosion resistance, UV stability |
| Architectural | Variety of color options, ease of maintenance | Window frames, doors, railings | Weather resistance, non-chalking |
| Industrial Equipment | Cost-effective, durable finish | Safety equipment, tools, machinery | Impact resistance, chemical tolerance |
| Furniture | Unique finishes, smooth textures | Chairs, tables, outdoor furniture | Scratch resistance, fade resistance |
| Electronics | Thermal management, excellent adhesion | Covers, enclosures, brackets | Electrostatic discharge (ESD) properties |

Powder coating is emerging as a sustainable alternative to traditional liquid coatings, offering notable environmental advantages. One of the most significant benefits is its lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. According to the Powder Coating Institute, powder coatings typically emit zero VOCs during application, making them a safer choice for both workers and the environment. In contrast, traditional liquid paints can release harmful solvents that contribute to air pollution and pose health risks, as highlighted in a study by the Environmental Protection Agency, which reports that VOCs from coatings are a major source of air quality issues.
Additionally, the powder coating process produces less waste than conventional methods. A report from the American Coatings Association notes that up to 15% of liquid coatings can be wasted during application due to over-spray, whereas powder coatings can reclaim up to 98% of the unused material through recycling techniques. This not only reduces material costs but also diminishes the environmental footprint associated with disposal of excess paint. Furthermore, powder coatings demonstrate exceptional durability and resistance to scratches, corrosion, and UV rays, decreasing the need for frequent repaints and thereby minimizing resource use over time. This combination of reduced VOC emissions, lower waste production, and longer-lasting finishes positions powder coating as a leading choice for environmentally conscious manufacturing and restoration across various industries.






