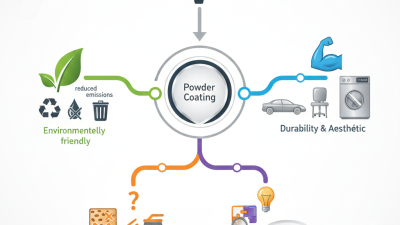
Plastic dip coating offers versatile applications in various industries, enhancing the durability and aesthetics of products. Dr. Emily Hart, a leading expert in polymer technology, states, "Plastic dip coating transforms materials, giving them both strength and visual appeal." This innovative process involves dipping objects into a liquid plastic solution. The plastic adheres to surfaces and forms a protective layer upon drying.
The versatility of plastic dip coating makes it suitable for automotive, electronics, and household goods. It can change the texture and color of any object while providing resistance to corrosion and wear. However, challenges exist in achieving uniform thickness and proper adhesion on complex shapes. These imperfections can affect the coating's performance.
Understanding the process is crucial. Plastic dip coating may seem simple, yet nuances determine its effectiveness. Exploring this method reveals both its strengths and areas needing improvement. Emphasizing quality control can elevate the outcomes. It's essential to reflect on these aspects as the industry evolves.


Plastic dip coating is a versatile process used to create a protective layer on various surfaces. This method involves immersing the object in a liquid plastic solution, which forms a durable coating once it cools down. A 2021 industry report indicated that the global plastic coating market is projected to reach over $30 billion by 2026, driven by increased demand in automotive and industrial applications.
One of the key advantages of plastic dip coating is its ability to enhance grip and aesthetics. Items like tools and handles often benefit from improved texture and color options. However, the finish can be susceptible to wear and tear over time. Certain environmental conditions can also impact the longevity of the coating, raising questions about its durability. Some users have reported issues with peeling or chipping after prolonged exposure to harsh elements.
While plastic dip coating offers numerous benefits, it is not without challenges. Achieving a uniform thickness can be difficult, especially for complex shapes. Inconsistencies in application may lead to weak spots. This variance can result in reduced protection effectiveness. Companies in the sector are continuously looking for ways to improve application techniques and materials. The journey toward innovation remains both promising and flawed.
Plastic dip coating has an intriguing history that spans several decades, evolving significantly since its inception. Initially developed in the 1950s, the technique was originally used for insulating electrical components. The flexibility and durability of the coating quickly caught the attention of various industries. By the 1980s, plastic dip coating was employed in automotive and household products. Recent reports indicate that the global plastic dip coating market is projected to reach $5.4 billion by 2027.
The materials used in plastic dip coating have also advanced over the years. Early formulations primarily relied on polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Today, manufacturers are exploring more sustainable options that reduce environmental impact. This shift reflects a growing industry need for eco-friendly practices. Not all developments have been smooth. Challenges such as adhesion and longevity of some new materials have prompted further research. While progress is evident, industry professionals still grapple with finding the perfect balance between performance and sustainability.
Despite its long-standing applications, plastic dip coating is not without limitations. For instance, variations in temperature can affect the coating's properties. Adverse conditions may lead to cracking or peeling over time. The quest for improved formulations continues, as the industry seeks to minimize these issues. The journey of plastic dip coating remains a fascinating tale of innovation intertwined with ongoing challenges.
This chart illustrates the growing interest in plastic dip coating from the 1980s to 2020. The increase in search interest indicates the expanding applications and awareness of this versatile protective coating method.
Plastic Dip Coating is a popular technique used to protect and enhance various surfaces. The key materials involved in this process greatly influence its effectiveness. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is one of the primary components. It acts as a flexible layer, offering excellent protection against corrosion and wear. PVC makes up about 35% of the coating’s composition.
Another significant material is ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). This polymer provides improved adhesion and durability. Reports indicate that coatings incorporating EVA show a 20% increase in longevity compared to those without it. Color pigments are also crucial in achieving the desired aesthetic. These pigments not only enhance appearance but also affect UV resistance and hardness.
Despite its advantages, some challenges exist. The flexibility of the coating can lead to issues in highly demanding environments. Moreover, achieving the right thickness can be tricky. An improperly applied layer may result in peel-off or inconsistencies. Each application requires careful attention to detail. Understanding the interaction of these materials is vital for optimal outcomes.
| Material Type | Description | Properties | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane | Flexible and durable coating commonly used for dip coating. | High elasticity, UV resistance, and chemical resistance. | Automotive coatings, tool grips, and sporting equipment. |
| Vinyl | A synthetic resin or plastic derived from polyvinyl chloride (PVC). | Waterproof, resistant to abrasion, and easy to apply. | Signage, protective coatings, and vehicle wraps. |
| Acrylic | Transparent plastic that can be used for protective coatings. | UV stable, weather-resistant, and good clarity. | Outdoor furniture, lighting fixtures, and signs. |
| Neoprene | Synthetic rubber used in various applications for its flexibility. | Good heat and chemical resistance, durable. | Wetsuits, hoses, and electrical insulation. |
Applying plastic dip coating is a detailed process. Start by selecting a clean, dry surface. Remove any dirt and grease thoroughly. This step prevents imperfections in the finish. Next, gather your materials, including the plastic dip spray or can, a mask, and gloves. Proper preparation prevents messy hands.
Now, it's time to apply the coating. Hold the spray can about 6-12 inches away from the surface. Begin with light, even coats. This is key for achieving a smooth finish. However, don’t rush. Take your time to ensure proper coverage. Aim for 3-4 thin layers instead of one thick coat. Thick coats can lead to runs and uneven spots.
After applying, allow each layer to dry before adding the next. Patience is crucial at this stage. It’s easy to overlook drying time, but this impacts durability. Once the final coat is dry, inspect your work. Look for any areas needing touch-ups. Mistakes can happen, and evaluating the finish helps improve future applications.
Plastic dip coating offers a versatile solution for various applications. It creates a rubber-like protective layer on surfaces. This coating improves durability against weather, chemicals, and wear. It also enhances grip and creates a smooth finish. These attributes make it popular in automotive, electrical, and household products.
One of the significant benefits is its ease of application. Users can apply it using spray cans or dipping methods. This accessibility encourages creativity in personal projects. For instance, hobbyists might customize tools or bike parts for a unique touch. However, not all applications are flawless. Over time, the coating can chip or wear off, requiring reapplication. This maintenance can be a hassle for some users.
Another aspect to consider is the aesthetic appeal. Plastic dip comes in various colors and finishes. This allows for personalization in many items, from car wheels to mobile phone cases. Yet, while it enhances appearance, it may not offer the same level of protection as other coatings. Users must weigh the pros and cons. The balance between beauty and durability can be a tricky decision.